
algae, and aquatic plants
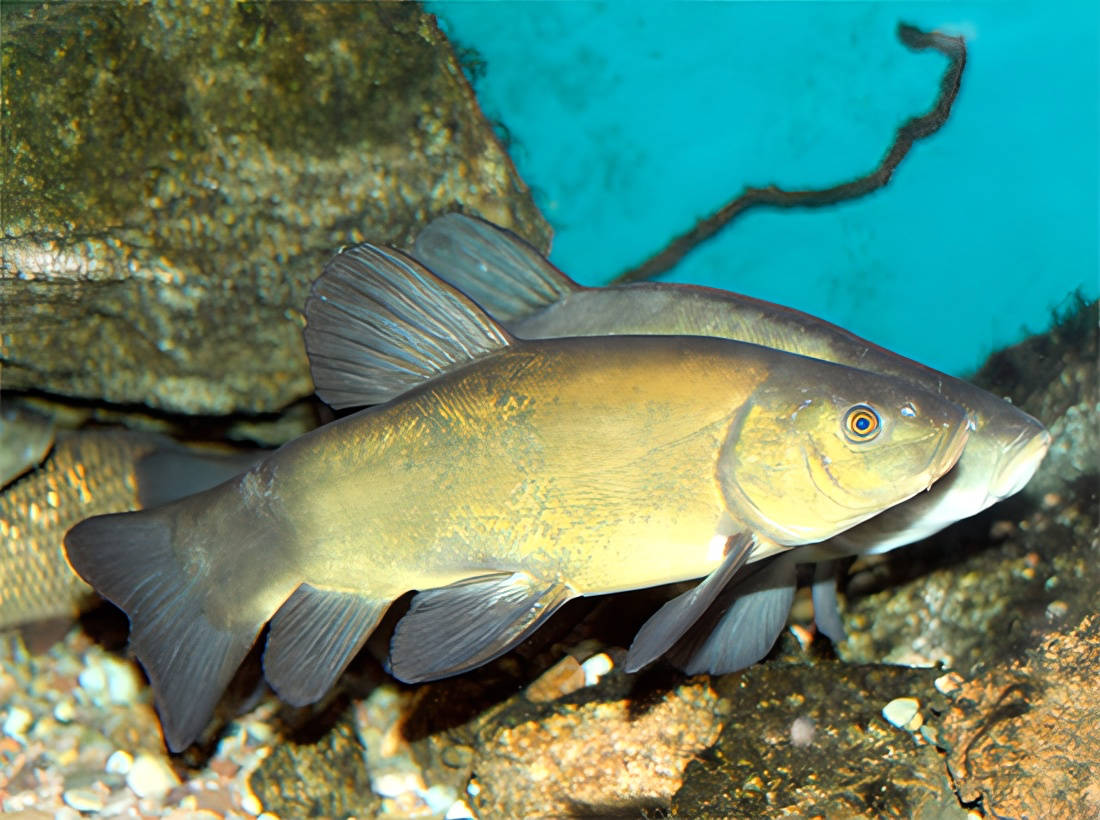
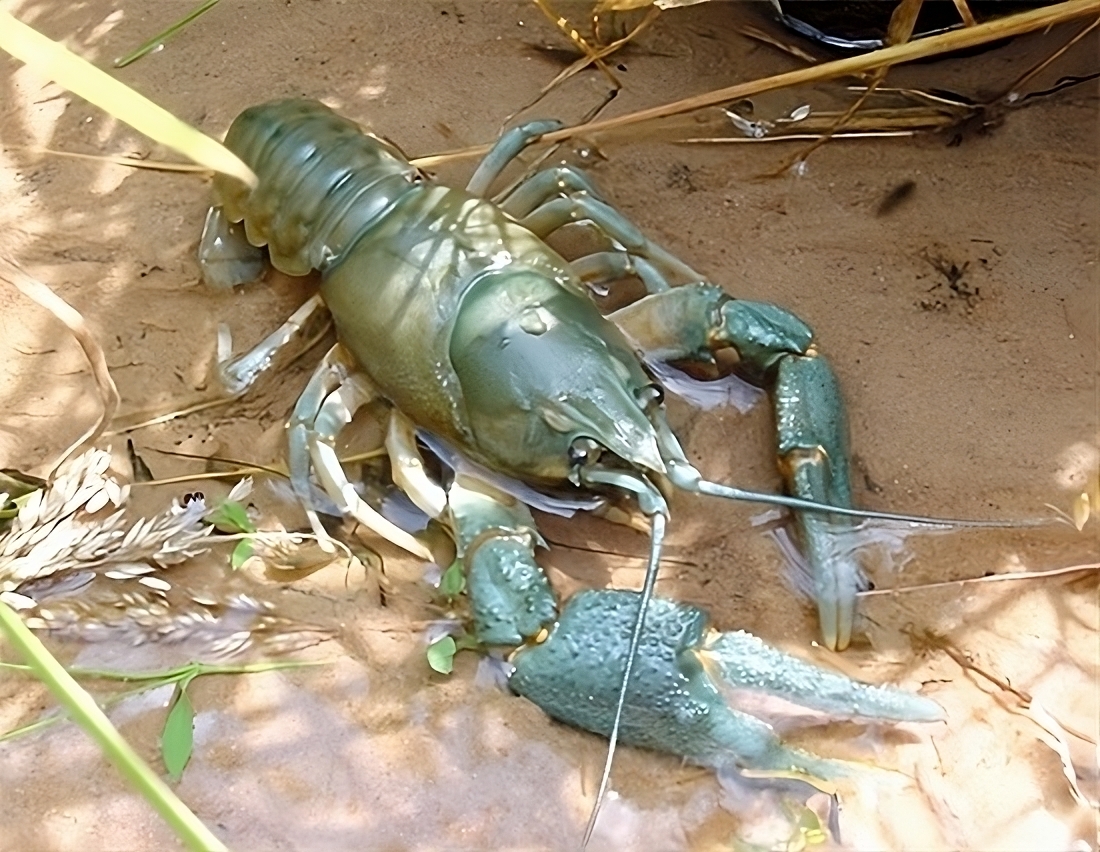








The main advantage of Biocaptech is that it does not cause any harmful effects on aquatic life. Unlike many other water treatment methods that can disrupt ecosystems and harm aquatic organisms, Biocaptech is designed to work in harmony with nature. It helps maintain biodiversity and preserves the health of fish, plants, and other forms of aquatic life present in treated environments.
Furthermore, Biocaptech offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional water treatment methods, such as the use of chemicals or costly and energy-intensive technologies. By opting for this process, it is possible to reduce the ecological footprint, minimize risks to human health, and contribute to the preservation of freshwater resources.
The effects of the Biocaptech process on living organisms have been carefully studied, and the results are very encouraging. Observations have shown no mortality among fish, mollusks, and crustaceans. This demonstrates that the Biocaptech process poses no toxic or harmful effects on these species, which are essential for maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Phytoplankton, a crucial component of the aquatic food chain, is also unaffected by the Biocaptech process. This means that microorganisms responsible for primary production in aquatic ecosystems continue to thrive, keeping the base of the food chain intact.
Moreover, daphnia, a type of small freshwater crustacean often used as an indicator of ecosystem health, experience no mortality during treatment with the Biocaptech process. In fact, an increase in the number of juveniles has been observed, indicating that this process may even support reproduction and population growth in daphnia.
By preserving the diversity and health of fish, mollusk, crustacean, and other organism populations, the process helps maintain ecosystem balance and biodiversity.
It is important to emphasize that these observations were made following rigorous studies and in-depth scientific monitoring.
Cyanobacteria:
Cyanobacteria can have harmful effects on the environment and human health. They can produce toxins dangerous to health, cause eutrophication of water bodies, create dead zones with a lack of oxygen, and disrupt human activities such as swimming and agriculture. Monitoring and managing cyanobacteria blooms are essential to minimize their negative impacts.